For Companies and Institutions
-
Commercial Banking
We provide credit, financing, treasury and payment solutions to help your business succeed. We also offer best-in-class commercial real estate services for investors and developers.
-
Global Corporate Banking
We help clients achieve their long-term strategic goals through financing, liquidity, payments, risk management and investment banking solutions.
-
Investment Banking
Providing investment banking solutions, including M&A, capital raising and risk management, for a broad range of corporations, institutions and governments.
-
Institutional Investing
We support the entire investment cycle with market-leading research, asset management, analytics, execution, and investor services.
-
Payments
Your partner for commerce, receivables, cross-currency, working capital, blockchain, liquidity and more.
Key Links
For Individuals
-
Wealth Management
With J.P. Morgan Wealth Management, you can invest on your own or work with an advisor to design a personalized investment strategy. We have opportunities for every investor.
-
Private Bank
A uniquely elevated private banking experience shaped around you.
Explore a variety of insights.
Key Links
Insights by Topic
Explore a variety of insights organized by different topics.
Key Links
Insights by Type
Explore a variety of insights organized by different types of content and media.
Key Links
We aim to be the most respected financial services firm in the world, serving corporations and individuals in more than 100 countries.
Key Links
- Payments
- Payments Unbound
- Payments Unbound - The digital magazine
- Payments Unbound Articles
- A Visual Timeline of International Trade Finance
Featuring future-thinking clients
Payments Unbound unites clients from a wide range of industries to bring you innovative insights that help you navigate the future of payments.
A visual timeline of international trade finance
Visual timeline
Back at the dawn of recorded history, when merchants began making their first forays into far-off markets, they needed working capital to fund their trading activities. This gave rise to trade finance, a catch-all term describing financial strategies that aim to help international commerce thrive. As civilization advanced, global trade and its financing co-evolved, with progress in one fueling developments in the other. Here’s how...
Letters of credit and promissory notes on clay tablets are the oldest known forms of trade finance. These formal promises to make a payment at a later date were used as they are today: To facilitate business activities and enhance trust.
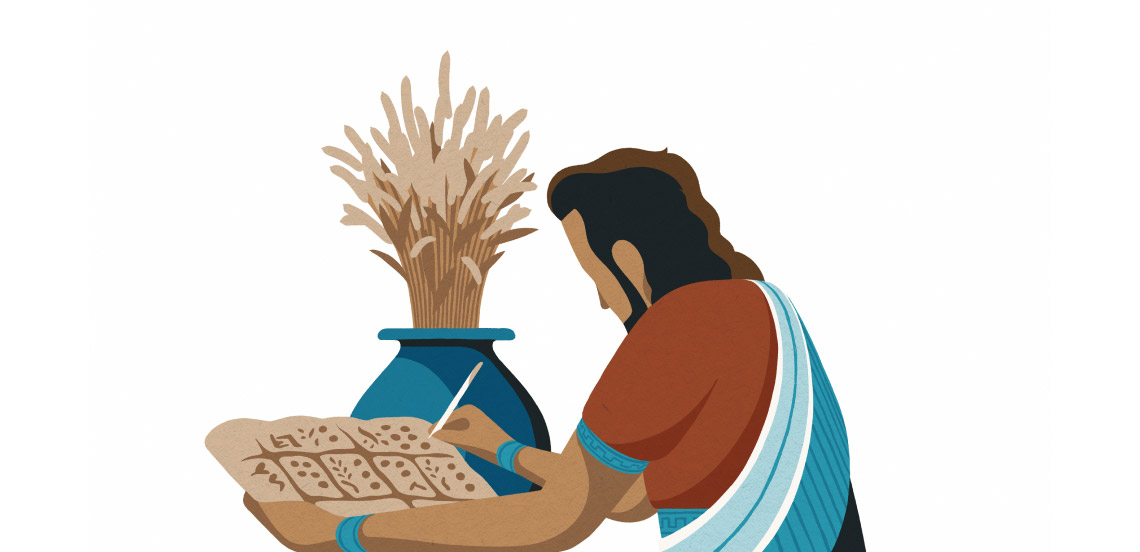

The Roman Empire established a robust legal framework, including contract regulations and rules around debt recovery, within which both trade and finance could flourish. Letters of credit were used to guarantee payment for goods shipped over long distances, contributing to extensive trade networks that spanned the Empire.

London became the heart of the trade finance world, and bills of exchange (a written unconditional agreement to pay a specified sum in the future) issued there supported transactions globally.
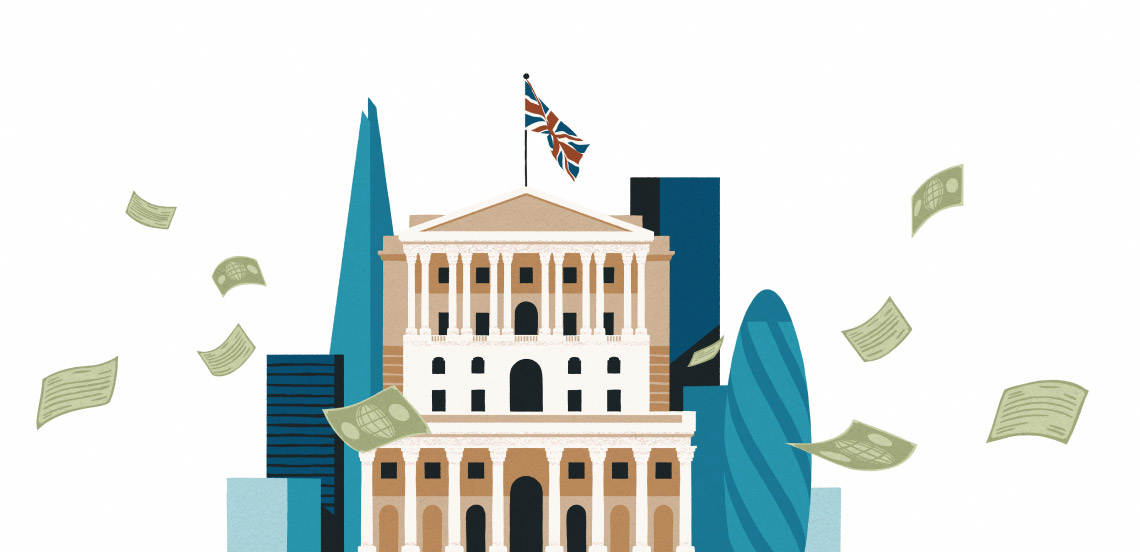

As the industrial revolution unfolded over the following 80 years, modern banking and credit models emerged, increasing the volume and velocity of global trade.

In 1821, the UK tied the British pound to a specific quantity of gold, leading other economies to adopt this as a standard. This international gold-based monetary system provided stability to international trade and investment.

The first formal export credit agency was established in the UK post-WW1 in response to economic disruptions, aiming to support national exporters and facilitate trade.

Established the rules for commercial relations between 44 countries. A new international monetary system was setup, in which the USD was tied to gold and other currencies tied to USD, and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World Bank were born.

The GATT was signed by 23 countries aiming to reduce tariffs and other barriers to promote international trade and economic recovery post-WWII.
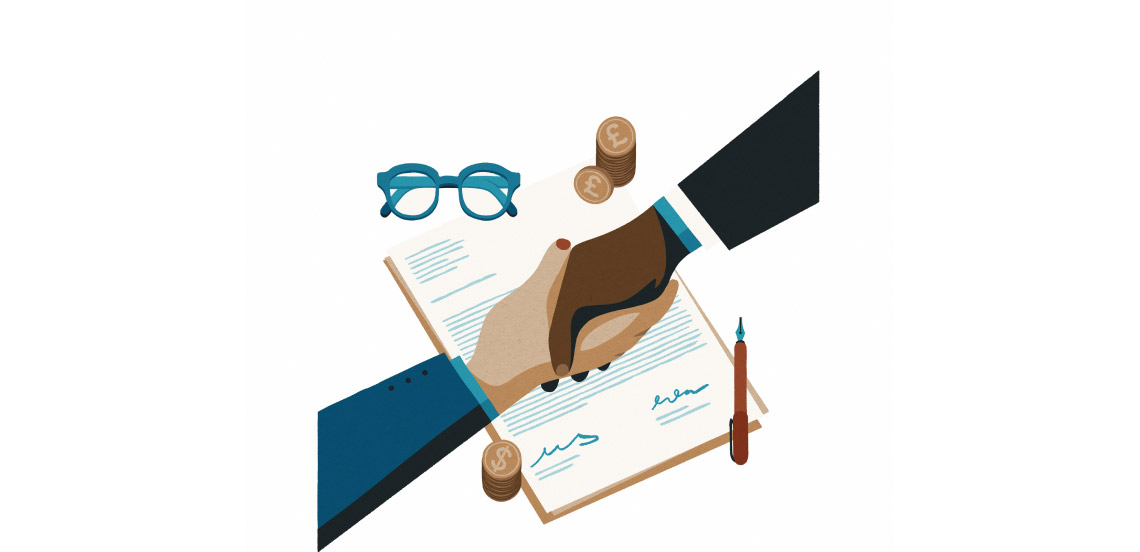

The use of traditional risk mitigation instruments such as letters of credit began to decline in favor of trade on open account terms, where goods are delivered before payment is made. Spurred by pacts such as the Southern Common Market Agreement and the North American Free Trade Agreement, alongside the emergence of major trading hubs in Singapore and Hong Kong, the rise of globalization in the 1980s and 1990s caused open account trading to surge.
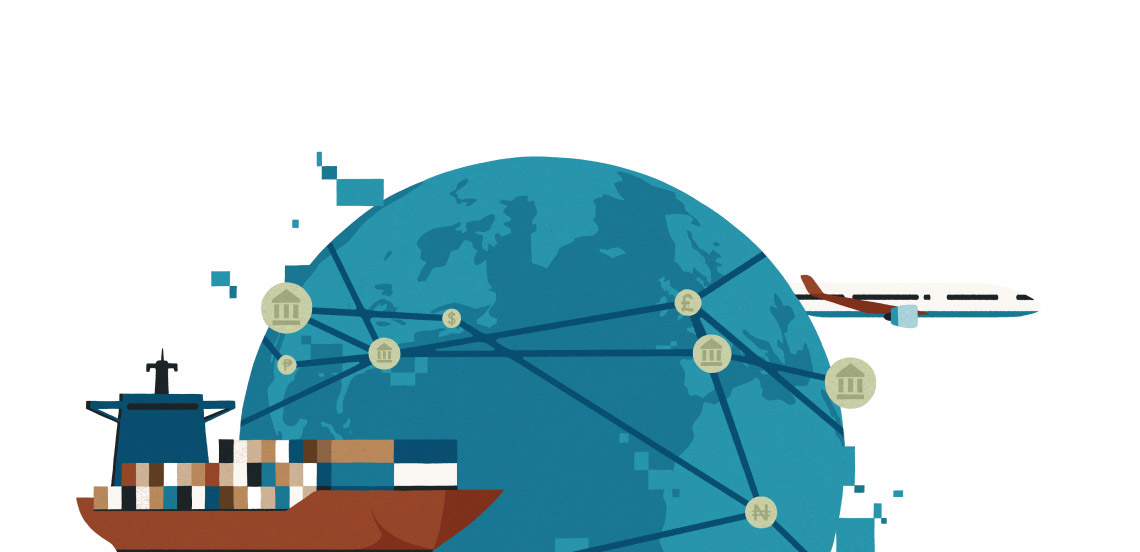

Aided by digital technologies, SCF allows buyers to extend payment terms while offering suppliers early payment on their invoices.

In 2017, the United Nations Model Law on Electronic Transferable Records (MLETR) was established. The UK and others then passed their own laws to legalise electronic bills of exchange and bills of lading (the latter being documents issued by carriers to acknowledge receipt of goods).

A multitude of AI innovations have recently emerged, such as optical character recognition for better document processing and checking, as well as generative AI tools for improving credit underwriting, particularly for smaller businesses.

Smart contracts, based on blockchain, may simplify operations including the issuance of letters of credit, management of supply chains, recordkeeping and document verification.

MAGAZINE
Volume 6: Open Banking Is Just Getting Started Volume 5: Game Changer Volume 4: Ready Payer One Volume 3: Bank to the Future Volume 2: The New World of Commerce Volume 1: The Money Revolution Browse all articlesWEBINARS
View all webinarsYou're now leaving J.P. Morgan
J.P. Morgan’s website and/or mobile terms, privacy and security policies don’t apply to the site or app you're about to visit. Please review its terms, privacy and security policies to see how they apply to you. J.P. Morgan isn’t responsible for (and doesn’t provide) any products, services or content at this third-party site or app, except for products and services that explicitly carry the J.P. Morgan name.