For Companies and Institutions
-
Commercial Banking
We provide credit, financing, treasury and payment solutions to help your business succeed. We also offer best-in-class commercial real estate services for investors and developers.
-
Global Corporate Banking
We help clients achieve their long-term strategic goals through financing, liquidity, payments, risk management and investment banking solutions.
-
Investment Banking
Providing investment banking solutions, including M&A, capital raising and risk management, for a broad range of corporations, institutions and governments.
-
Institutional Investing
We support the entire investment cycle with market-leading research, asset management, analytics, execution, and investor services.
-
Payments
Your partner for commerce, receivables, cross-currency, working capital, blockchain, liquidity and more.
Key Links
For Individuals
-
Wealth Management
With J.P. Morgan Wealth Management, you can invest on your own or work with an advisor to design a personalized investment strategy. We have opportunities for every investor.
-
Private Bank
A uniquely elevated private banking experience shaped around you.
Explore a variety of insights.
Key Links
Insights by Topic
Explore a variety of insights organized by different topics.
Key Links
Insights by Type
Explore a variety of insights organized by different types of content and media.
Key Links
We aim to be the most respected financial services firm in the world, serving corporations and individuals in more than 100 countries.
Key Links
- Payments
- Payments Unbound
- Payments Unbound - The digital magazine
- Payments Unbound Articles
- Evolution & Future of Payment Rails (Visual Timeline)
Featuring future-thinking clients
Payments Unbound unites clients from a wide range of industries to bring you innovative insights that help you navigate the future of payments.
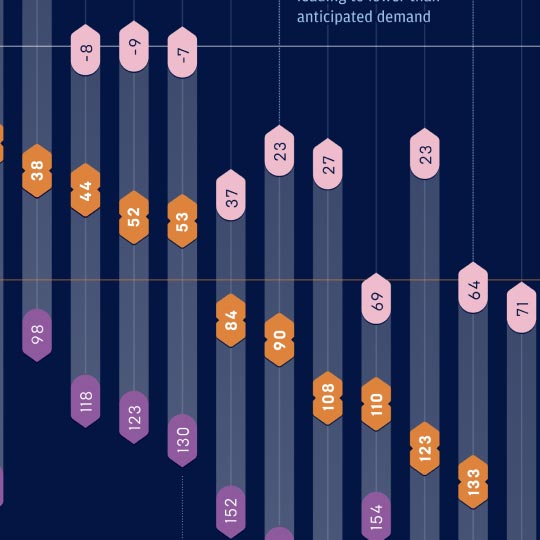
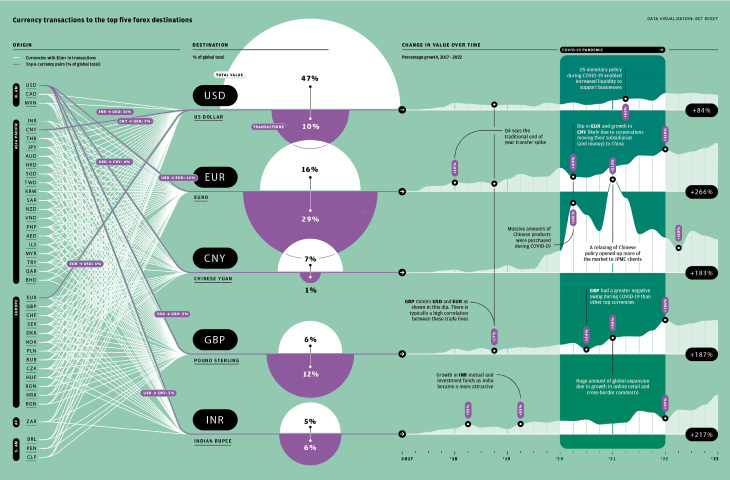
Tracking the evolution of payment rails
Visual timeline
Payment rails are the underlying networks and infrastructure that enable funds to get from A to B without the transfer of physical money. They ensure that when a payment is initiated by one person or institution, it is received by the intended beneficiary. From wire transfers and cards to online transactions and real-time settlement, payment rails have experienced a dramatic evolution.
By Wired
SOURCES: AS PER WIRED, MAY 2024
ILLUSTRATION: ADRIÀ VOLTÀI
MAGAZINE
Volume 5: Game Changer Volume 4: Ready Payer One Volume 3: Bank to the Future Volume 2: The New World of Commerce Volume 1: The Money Revolution Browse all articlesWEBINARS
View all webinarsYou're now leaving J.P. Morgan
J.P. Morgan’s website and/or mobile terms, privacy and security policies don’t apply to the site or app you're about to visit. Please review its terms, privacy and security policies to see how they apply to you. J.P. Morgan isn’t responsible for (and doesn’t provide) any products, services or content at this third-party site or app, except for products and services that explicitly carry the J.P. Morgan name.